
Haloperidol (Haldol)
Mechanism of action
Antipsychotic (butyrophenone derivative; first generation).
Non-selective blockade of dopaminergic Dreceptors in the brain.
Some alpha-adrenoreceptor and muscarinic receptor blockade.
Highly potent with very high extrapyramidal toxicity and low sedative action.
Very low hypotensive effect.
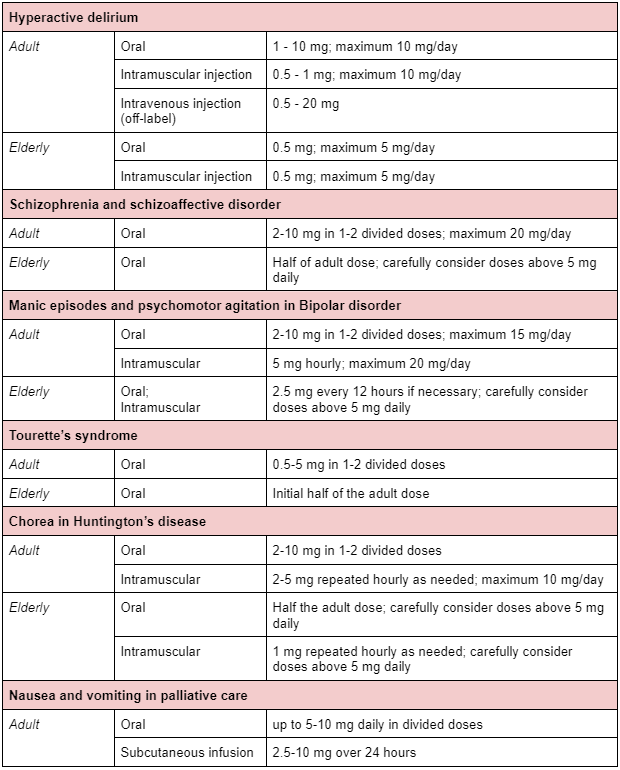
Indications and dose
Contraindications
Parkinson’s disease
Severe CNS depression
Dementia with Lewy bodies
Long QTc
Side-effects
Extrapyramidal symptoms, parkinsonism
Involuntary body movements
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Amenorrhea, galactorrhea, impotence, hyperprolactinemia
QT interval prolongation
Constipation
Dry mouth
Drowsiness
Oculogyric crisis
Postural hypotension
Precautions
Additive effect with other sedative drugs, alpha-adrenoreceptor blockers, anticholinergics.
Pharmacokinetics
Onset of action: peak in 30 minutes
Duration of action: mean 2 hours
Bioavailability: Oral: 60-70%
Distribution: 90% protein bound
Metabolism: Hepatic
Half-life of elimination: 14-26 hours
Excretion: Urine
Directions for administration
Lactate for intravenous or intramuscular administration.
Decanoate only for intramuscular administration - must not be administered intravenously.
Medicinal forms
Tablet - 1.5 mg tablets
Intravenous - 1 vial = 5mg in 1 ml
Injection oil (decanoate)
Injection solution (lactate)
Drops - 2mg in 1 ml
References





